
Home telehealth programs can help patients manage chronic disease, while receiving education and daily guidance from a nurse care coordinator or other health professional.
For some reason, however, many patients in home telehealth programs do not adhere to daily check-ins.
I am the telehealth specialist and facility e-consult coordinator with the Phoenix Veterans Administration Health Care System. As part of my studies toward a doctoral degree in nursing, I have found a potential solution.
My evidence-based quality improvement project addressed the question: Will implementing electronic daily reminders to document health status improve adherence to the program requirements?
Low response rates in the home telehealth (HT) programs in general have been an issue for years. I wanted to see what evidence exists on the topic of telehealth adherence and utilization, and what methods have been tested and proven to increase patient adherence to program requirements.
I found sufficient scientific support for the use of text messages and other daily electronic reminders to increase patient adherence to various health-related activities, such as taking vitamins, applying sunscreen, doing breast self-exams, and other self-adherence activities.
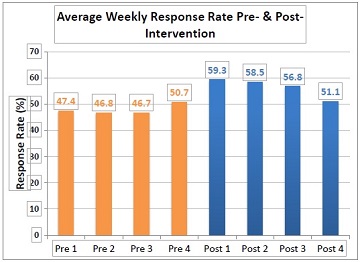 To test the concept of electronic daily reminders, I implemented the intervention with 40 Veterans with the Phoenix Veterans Administration Health Care System, whose home-telehealth response rates were below 70 percent.
To test the concept of electronic daily reminders, I implemented the intervention with 40 Veterans with the Phoenix Veterans Administration Health Care System, whose home-telehealth response rates were below 70 percent.
Over a four-week period, the Veterans received an electronic daily reminder sent to their HT device, to see what impact the reminders would have on their HT response rates. The goal of the HT program is for patients to respond daily, and the VA requirement is to have a minimum of 70 percent of HT patients reach that goal.
As I expected, my project showed that electronic daily reminders improved patient adherence to HT monitoring.
After four weeks of the intervention, 24 of the 40 participants – 60 percent -showed an increased HT response rate, with the average response rate improving significantly from 48.1 percent to 56.6 percent.
In addition, 14 participants – 35 percent - achieved at least a 70 percent response rate post-intervention.
I’ve concluded that the cost-effective intervention of implementing electronic daily reminders may be the answer for home telehealth programs struggling to increase the participation rates of their patients.
As a result, The Phoenix VA telehealth department has chosen to continue this intervention by adapting it to its standard operating procedure.


